
- 1st Dec
- 3 min read
Empowering Organizations with AI-Centric Transformation through Social Objects in Microsoft Copilot
In today’s competitive landscape, organizations are seeking to harness the power of AI to drive productivity and gain a competitive edge. Microsoft Copilot stands as a transformative tool that enables organizations to pivot towards an AI-centric approach, revolutionizing the way they leverage technology for enhanced efficiency and innovation. At the heart of Copilot lies a semantic search powered by Microsoft Graph, which serves as the cornerstone for contextual understanding and elevated search experiences within Microsoft 365 applications.
Empowering Semantic Search with Microsoft Graph: Microsoft Graph plays a pivotal role in enabling the semantic search capabilities within Copilot. By leveraging the capabilities of Microsoft Graph, Copilot delivers personalized and contextually relevant search results, empowering users to access information based on their organizational connections. This semantic understanding enhances productivity and drives efficiency within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, positioning organizations for success in the era of AI-driven operations.
Understanding the Dynamics of Microsoft Graph: Microsoft Graph operates as a unified programmability model, providing developers with seamless access to a diverse array of Microsoft 365 data and services. It acts as a gateway for interacting with resources and entities across the Microsoft ecosystem, offering a consistent and efficient means of retrieving and manipulating data across various applications and services. The rich capabilities of Microsoft Graph underpin the semantic search functionalities within Copilot, elevating the search experiences for users and driving organizational productivity.
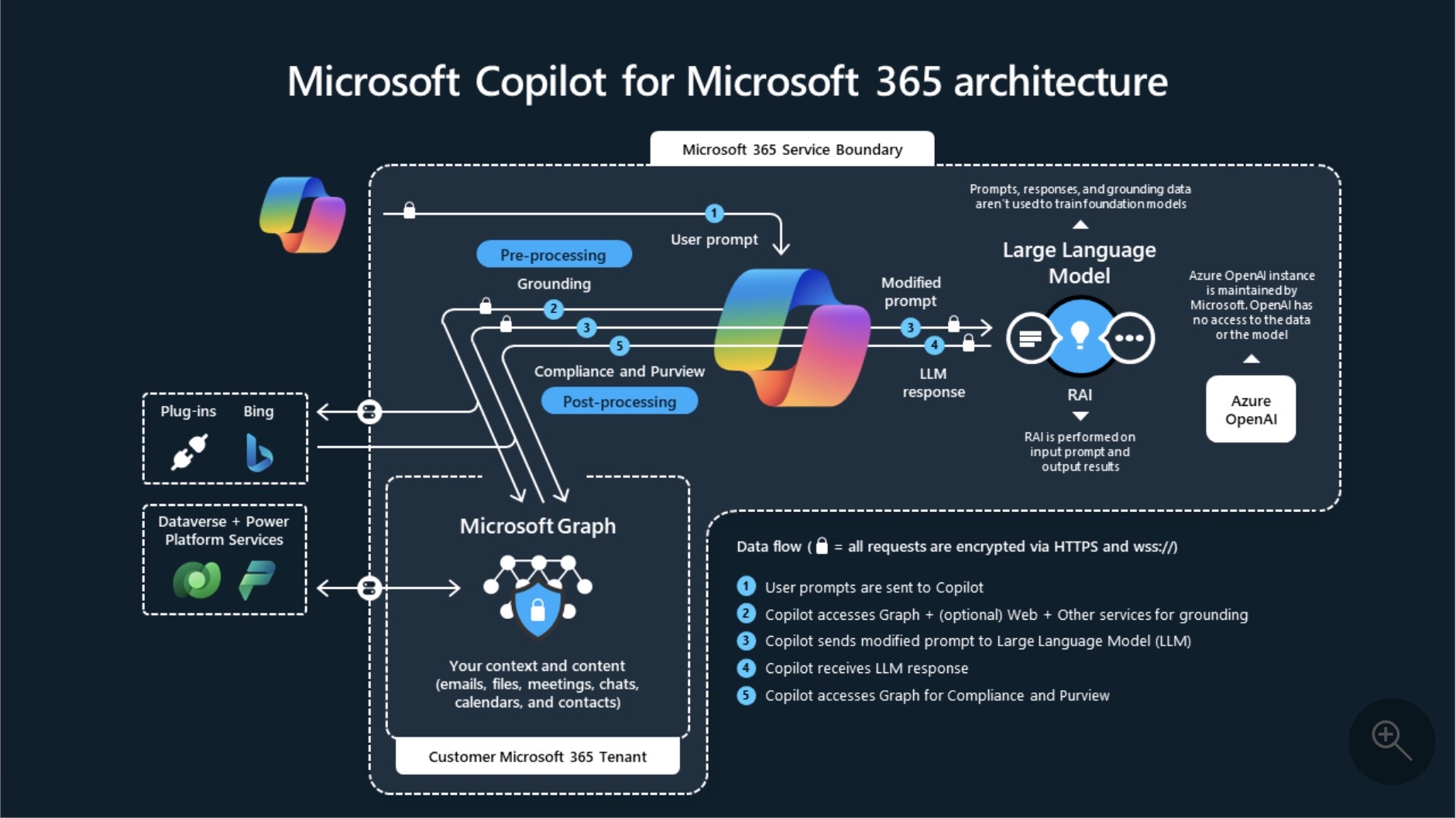
Challenges and Limitations of Microsoft Graph:
While Microsoft Graph serves as a robust foundation for data connectivity and insights, it is not without its challenges. Complex relationships, data quality assurance, and interoperability concerns pose significant hurdles in accurate relationship identification and semantic understanding within the Microsoft ecosystem. These limitations can impact the accuracy and efficiency of AI-driven solutions, necessitating a strategic approach to address these challenges.
Challenges and Limitations of Microsoft Semantic Search

Introducing SONN: Revolutionizing Data Classification in Microsoft Copilot
To address the limitations and challenges posed by Microsoft Graph, we introduce the Social Object Neural Network (SONN). SONN represents a paradigm shift in data classification, leveraging a five-class taxonomy—People, Things, Services, Locations, and Activities—to streamline data organization and relationship management within Microsoft Copilot. By implementing SONN, organizations can unlock the full potential of AI-centric operations, driving efficiency and innovation in their workflows.
Implementing SONN in Microsoft Graph: The integration of SONN into Microsoft Graph involves a structured approach to data modeling, schema design, metadata annotations, and relationship definitions. By mapping existing data entities to the five-class taxonomy and updating entity structures to align with the defined classes, organizations can streamline data access and relationship identification within the Microsoft ecosystem. SONN offers a clear framework for interpreting data relationships and associations, enhancing semantic understanding and driving operational efficiency.
Use Case Scenario: Employee Resource Management System
Microsoft Graph without SONN
1. Current Approach:
* Data Entities: Employees, Departments, Projects, Tasks.
* Relationships:
* Employees are associated with Departments.
* Employees work on Projects assigned to them.
* Projects consist of Tasks assigned to employees.
2. Steps: a. Employee Search:
* Query Microsoft Graph for employee details.
* Retrieve employee data along with department, project, and task information.
3. b. Project Allocation:
* Assign a new project to an employee.
* Update project details in the system.
4. Challenges:
* Complex Relationships: Navigating relationships between employees, departments, projects, and tasks can be intricate and require extensive querying.
* Semantic Clarity: Ambiguity in how data entities are related may lead to challenges in interpreting and utilizing the data effectively.
* Data Organization: Without clear classification, managing and accessing data across multiple entities can be cumbersome.
Use Case of Microsoft Graph Working with the Five Classes Taxonomy:
1. Enhanced Approach with Five Classes Taxonomy:
* Classes: People (Employees), Things (Projects, Tasks), Services (Departments), Locations, Activities.
* Relationships:
* Employees belong to Departments (Services).
* Projects (Things) are assigned to Employees (People).
* Locations for Activities (Tasks) within Projects.
2. Steps: a. Employee Search:
* Query Microsoft Graph for employee details within the People class.
* Retrieve associated Department (Service) information for each employee.
3. b. Project Allocation:
* Assign a new project (Thing) to an employee (Person) within the relevant Department (Service).
* Update project details in the system. 4. Advantages:
* Clear Data Classification: Data entities are categorized into distinct classes, simplifying data organization and relationship identification.
*
Structured Relationships: Defined relationships within each class facilitate efficient navigation and querying of data connections.
* Improved Semantic Understanding: The taxonomy enhances semantic interpretation by providing a structured framework for data relationships.
Comparison:
* Efficiency: The taxonomy-based approach streamlines data access and relationship identification, reducing complexity and enhancing semantic clarity in managing data entities.
* Scalability: With well-defined classes, scaling the system and adding new data entities becomes more manageable and structured.
* User Experience: Users can navigate and interact with data more intuitively, leading to improved usability and productivity in accessing information.
By applying the five classes taxonomy in Microsoft Graph, organizations can optimize data management, streamline relationship identification, and enhance semantic understanding within their systems, ultimately improving operational efficiency and user experience.
As explained above the current Microsoft Copilot is challenged by complex data relationships leading to inefficiencies in employee allocation and project management. With SONN, a clear classification into five distinct classes simplifies data access and relationship identification. Resulting in improved semantic understanding and structured data navigation driving operational efficiency, enhancing productivity and streamlining workflows.
Empowering Your AI-Centric Journey: Embark on your journey towards an AI-centric organization by embracing SONN in Microsoft Copilot. Enhance data accuracy, streamline relationships, and unlock the true power of AI. Contact us today to learn more about how SONN can revolutionize your organization’s data strategy with Microsoft Copilot. Let’s shape a smarter future together.